why is sodium low in dka Ketoacidosis diabetic bicarbonate sodium diabetestalk nejm
Today, I want to talk about a topic that is quite important in the medical field - Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, characterized by high blood sugar levels, ketones in the urine, and metabolic acidosis. It requires immediate medical attention and treatment. Recently, I came across some interesting information regarding the use of sodium bicarbonate and the measurement of serum versus total body potassium in the management of DKA.
Sodium Bicarbonate in DKA
 There has been a long-standing debate among healthcare professionals regarding the use of sodium bicarbonate in the treatment of DKA. Sodium bicarbonate is an alkaline substance that can help correct acidosis, which is a common complication of DKA. However, its use in DKA has been a topic of debate due to conflicting evidence and potential risks.
There has been a long-standing debate among healthcare professionals regarding the use of sodium bicarbonate in the treatment of DKA. Sodium bicarbonate is an alkaline substance that can help correct acidosis, which is a common complication of DKA. However, its use in DKA has been a topic of debate due to conflicting evidence and potential risks.
According to an article from REBEL EM - Emergency, the use of sodium bicarbonate in DKA is controversial. The authors highlight that bicarbonate administration has not been shown to improve patient-oriented outcomes, such as mortality or hospital length of stay. In fact, it may be associated with an increased risk of adverse events, such as cerebral edema. Therefore, current guidelines recommend reserving the use of sodium bicarbonate for severely acidemic patients with a pH less than 6.9.
Measurement of Serum vs. Total Body Potassium
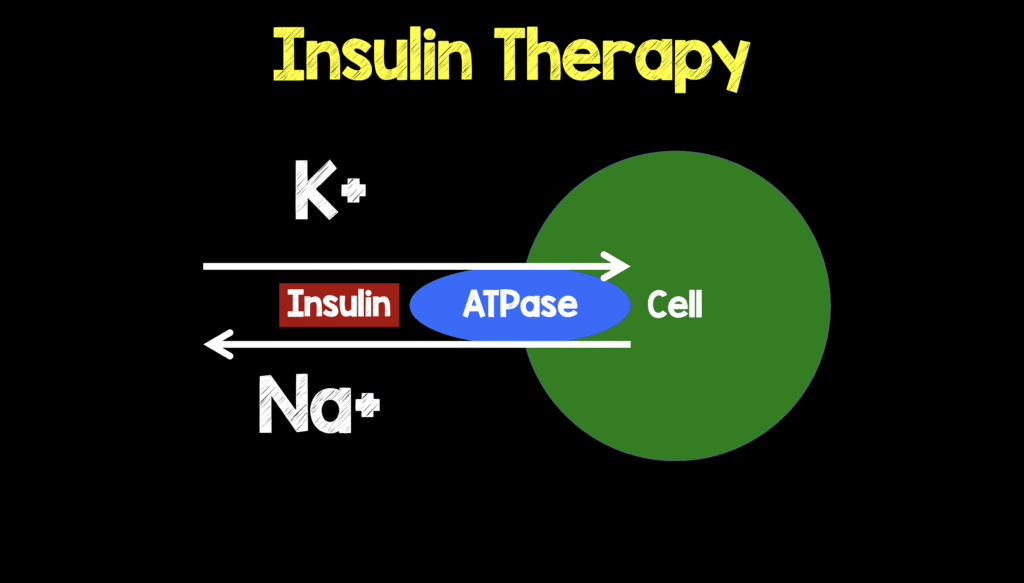 When managing DKA, measuring potassium levels is crucial as both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia can occur. Traditionally, serum potassium levels have been used to guide treatment decisions. However, recent evidence suggests that measuring total body potassium might provide a more accurate assessment of potassium status in patients with DKA.
When managing DKA, measuring potassium levels is crucial as both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia can occur. Traditionally, serum potassium levels have been used to guide treatment decisions. However, recent evidence suggests that measuring total body potassium might provide a more accurate assessment of potassium status in patients with DKA.
In an insightful article by Medicine Specifics, the authors explain that serum potassium levels may not accurately reflect total body potassium stores. Factors such as acidosis and insulin deficiency in DKA can shift potassium from the intracellular to extracellular compartments, leading to an increase in serum potassium levels despite whole-body potassium depletion. Therefore, they advocate for the measurement of total body potassium, such as through 24-hour urinary potassium excretion or calculations, to assess potassium status and guide appropriate potassium replacement.
In summary, the use of sodium bicarbonate in DKA remains controversial, with current guidelines recommending its limited use in severely acidemic patients. Additionally, recent evidence suggests that measuring total body potassium may provide a more accurate assessment of potassium status in patients with DKA. As with any medical condition, it is important to stay updated with the latest research and guidelines to provide the best possible care to patients.
If you are looking for Any Benefit to Sodium Bicarbonate in DKA? - REBEL EM - Emergency you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about Any Benefit to Sodium Bicarbonate in DKA? - REBEL EM - Emergency like How Does Ketoacidosis Work | DiabetesTalk.Net, Serum vs. Total Body Potassium in DKA | Medicine Specifics and also SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow. Here you go:
Any Benefit To Sodium Bicarbonate In DKA? - REBEL EM - Emergency
 rebelem.combicarbonate sodium dka evaluating rebelem
rebelem.combicarbonate sodium dka evaluating rebelem
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic diabetic inhibitor induced pathophysiology dka urine renalfellow renal sediment mitochondria acidosis immunologic transplantation principles bacterial variant
How To Avoid Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Diabetes Strong
 diabetesstrong.comdka ketoacidosis diabetic avoid
diabetesstrong.comdka ketoacidosis diabetic avoid
Serum Vs. Total Body Potassium In DKA | Medicine Specifics
 medicinespecifics.comdka potassium insulin ketoacidosis myths hypokalemia sodium
medicinespecifics.comdka potassium insulin ketoacidosis myths hypokalemia sodium
How Does Ketoacidosis Work | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic bicarbonate sodium diabetestalk nejm
diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic bicarbonate sodium diabetestalk nejm
Any benefit to sodium bicarbonate in dka?. Dka potassium insulin ketoacidosis myths hypokalemia sodium. Bicarbonate sodium dka evaluating rebelem